All but Which of the Following Describe the Reticular Formation
It filters stimuli and passes on important signals. The reticular activating system RAS extends upward through the medulla the pons and the midbrain and into the hypothalamus.

Reticular Formation Definition Functions Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
This part of the brain is involved in eating sleeping and when you become aroused.

. Its functions are primarily that of regulating the sleepwake cycle and assist in. The fact that alcohol often causes problems with balance and coordination suggests that it may have an effect on the. - reticulospinal tract descends from the pontine reticular formation down the medial longitudinal fasciculus and then in the anterior funiculus of the spinal cord.
Today the reticular formation is considered to play a very important role in different activities of the brain and the nervous system. The reticular formation is well developed in all vertebrates and it forms the core of the brain-stem in. It is primarily responsible for visual perception.
It is the master endocrine gland of the brain. Function of the reticular formation. All but which of the following describe the reticular formation.
The best which describes the reticular formation of the brain is. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. B Describe how each of the following are related to the results of the written test.
Cardiovascular control The reticular formation includes the cardiac and vasomotor centers of the medulla oblongata. Reticular Formation- Is made of nerve cells running from spinal cord to brain stem and then to thalamus. The bulbar synchronizing region facilitates reflex and.
All of the following are properly paired except. Role in sleep and wakefulness cycle It plays a central role in states of consciousness like alertness Controls muscle tone Role in visceral function Influences EEG Influences learning Influ. Select all that apply a.
All of the following describe the reticular formation EXCEPT. It is responsible for regulating consciousness skeletal muscles respiratory muscles and facial. All of the following describe the reticular formation except.
Cerebellum- controls coordination of muscular activity. The dendrites are polysynaptic giving rise to the reticular formation being described as a non-specific unit. The nerve fibers in these pathways act in the spinal cord to block the.
B gracile nucleus - relays somatic sensory information to the thalamus. Both efferent and afferent fibers interact with the reticular formation to. Phineas gage showed severe personality changes following an accident that damaged his.
D cuneate nucleus - relays somatic sensory information to the thalamus. Brain stem - part of brain between spinal cord and diencephalon Reticular formation - pathway through brainstem that carries sensory information to higher brain centers Network of neurons that is involved in taking sensory information Where white and gray matter extend through brain stem Extend from superior spinal cord through brain stem and into inferior diencephalon. Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area.
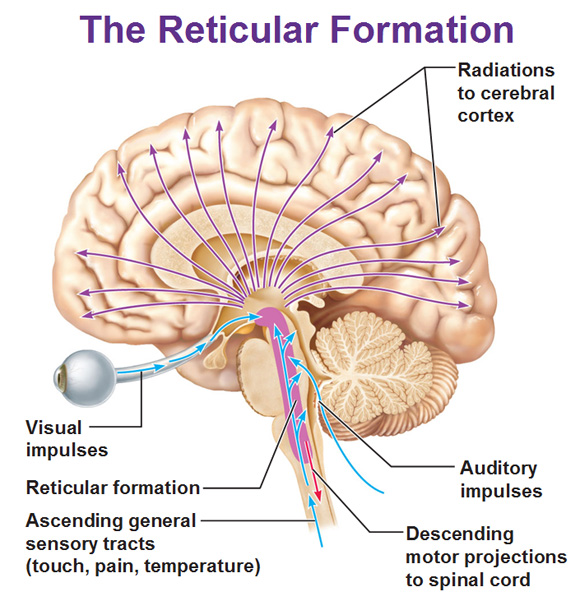
A diffuse collection of neurons that extend through the central core of the brainstem from medulla to midbrain. This part of the central nervous system spread in three main columns from one end of the brainstem to the other is a core relay point that connects the nerves of the spinal cord with. The reticular formation is located in the portion of the brainstem known as the pons.
The neurons have large dendrites that extend long distances to receive and integrate synaptic input from almost all of the axons that project to or through the brainstem. Which of the following statements accurately describe the physiology of sleep. Reticular formation Predictive validity Semantic memory.
Pain modulation The reticular formation is one means by which pain signals from the lower body reach the cerebral cortex. The dendrites and axons of the reticular formation are atypical when compared to those of other neurons. The reticular formation is a complex network of brainstem nuclei and neurons that serve as a major integration and relay center for many vital brain systems to coordinate functions necessary for survival.
The thalamus routes all of the following senses for processing in the cerebral cortex EXCEPT. The reticular formation is a network of reticular nuclei ascending tracts and descending tracts. A reticular formation - located in the medulla oblongata.
Earlier no particular function was known to be associated with the reticular formation. 1 medial reticulospinal pontine. The medullas function is.
The term reticular formation refers to portions of the brain stem core characterized structurally by a wealth of cells of various sizes and types arranged in diverse aggregations and enmeshed in a complicated fiber network. The reticular formation is a neuron network in the brainstem that enables consciousness sensory and motor function and endocrine and neurotransmitter regulation. Definitions without application do not score.
Reticular formation as the name suggests is a network of neurons and nerve fibers present in the brain. After a neuron fires about how long is its refractory period. It is also the origin of the descending analgesic pathways.
One-thousandth of a second. C ascending tracts - carry motor information to the thalamus. What is the reticular formation.
Controlling vital reflexes such as respiration heart rate and blood pressure. The axons are extremely long and can reach sites far removed from their cell bodies. Answers must be presented in sentences and sentences must be cogent enough for students meaning to be apparent.
It is mainly involved in motor coordination and balance.

Reticular Formation Function Location What Is The Reticular Formation Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Reticular Formation And Limbic System Textbook Of Clinical Neuroanatomy 2 Ed
No comments for "All but Which of the Following Describe the Reticular Formation"
Post a Comment